China is celebrating its eighth Space Day, which falls on April 24 each year. Over the past decade, the nation has made remarkable achievements in space exploration.
TIAN CHI/CHINA DAILY
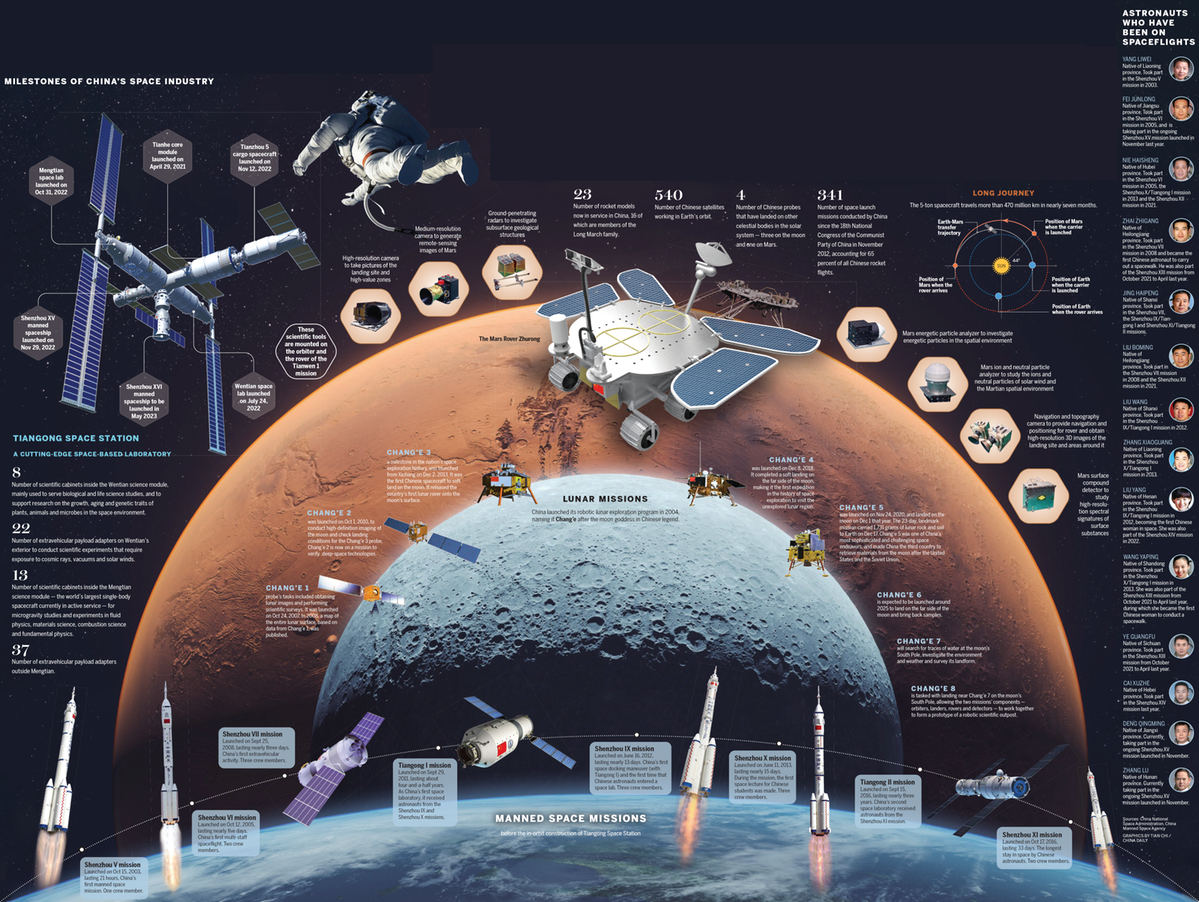
Milestones
Dec 2, 2013
The Chang'e 3 mission begins, with the aim of sending a robotic probe to the moon. After a 12-day flight, the probe lands, becoming the first Chinese spacecraft to achieve the feat and the first craft from any country to achieve the goal in nearly four decades. Yutu, the first Chinese lunar rover, moves onto the lunar soil on Dec 15 and begins operations. It works until July 2016.
Dec 8, 2018
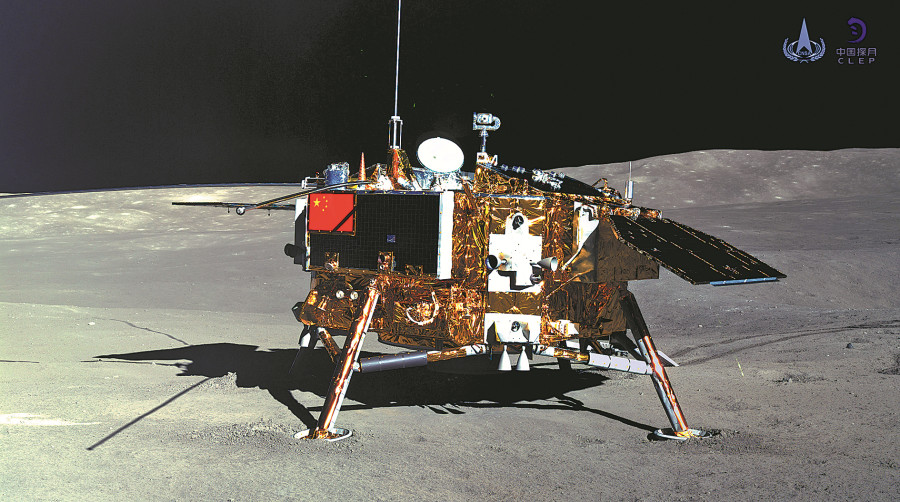
China's fourth lunar probe, Chang'e 4, is launched toward the far side of the moon. After a 26-day journey, the robotic spacecraft lands in the Von Karman crater, beginning humanity's first close observation of the area. The Yutu 2 rover has worked on the moon for nearly 1,600 days and traveled more than 1,500 meters on the lunar soil, making it the longest-working rover ever.
June 5, 2019
A Long March 11 solid-propellant carrier rocket is used for China's first seaborne space launch in its territorial waters. Prior to the mission, the country has conducted more than 310 carrier rocket launches at its four land-based space launch centers. So far, China has conducted five sea-based launches.
July 25, 2019
i-Space, a Beijing startup, becomes the first private enterprise in China to successfully conduct an orbital mission. The company launches its first SQX-1 carrier rocket from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, sending two satellites and three experimental payloads into space. So far, three private Chinese rocket makers have conducted eight successful orbital missions.
July 23, 2020
The Tianwen 1 mission, the nation's first independent interplanetary exploration, is launched from Wenchang. It travels more than 470 million kilometers before entering Mars' orbit in February 2021. Its rover,named Zhurong, touches down on the planet on May 15, 2021, and begins work on the surface a week later.So far, the rover has traveled more than 1,900 meters and obtained a great deal of raw data.
July 31, 2020
The domestically developed Beidou Navigation Satellite System is completed and starts providing full-scale global services. Since 2000,more than 60 Beidou satellites have been launched, and some have been retired. Beidou is now one of the two space-based navigation networks with global coverage — the other being GPS from the United States.
Nov 24, 2020
The Chang'e 5 robotic moon mission is launched from the Wenchang Space Launch Center. After landing on Dec 1, it brings 1,731 grams of lunar rock and soil back to the Earth on Dec 17, about 44 years after the last lunar substances were returned. The 23-day mission makes China the third country to retrieve lunar samples.
April 29, 2021
In-orbit construction of the Tiangong space station begins as the Tianhe core module — the first and central component — is launched. The module has three parts: a connecting section; a life-support-and-control section; and a resources section. The capsule is bigger and heavier than any other Chinese spacecraft launched before it.To date, 12 astronauts have lived in the craft.
Dec 31, 2022
President Xi Jinping announces the completion of the Tiangong space station in his New Year address, marking the realization of a grand aspiration pursued by Chinese scientists and space industry workers for three decades.The station consists of three major components — a core module and two science lab modules — and has an overall weight of nearly 100 metric tons. It is designed to operate for more than 10 years.
Lunar missions
China launched its robotic lunar exploration program in 2004, naming it Chang'e after the moon goddess in Chinese legend.
Chang'e 1 probe's tasks included obtaining lunar images and performing scientific surveys. It was launched on Oct 24, 2007. In 2008, a map of the entire lunar surface, based on data from Chang'e 1, was published.
Chang'e 2 was launched on Oct 1, 2010, to conduct high-definition imaging of the moon and check landing conditions for the Chang'e 3 probe. Chang'e 2 is now on a mission to verify deep-space technologies.
Chang'e 3, a milestone in the nation's space exploration history, was launched from Xichang on Dec 2, 2013. It was the first Chinese spacecraft to soft land on the moon. It released the country's first lunar rover onto the moon's surface.
Chang'e 4 was launched on Dec 8, 2018. It completed a soft landing on the far side of the moon, making it the first expedition in the history of space exploration to visit the unexplored lunar region.
Chang'e 5 was launched on Nov 24, 2020, and landed on the moon on Dec 1 that year. The 23-day, landmark mission carried 1,731 grams of lunar rock and soil to Earth on Dec 17. Chang'e 5 was one of China's most sophisticated and challenging space endeavors, and made China the third country to retrieve materials from the moon after the United States and the former Soviet Union.
Chang'e 6 is expected to be launched around 2025 to land on the far side of the moon and bring back samples.
Chang'e 7 will search for traces of water at the moon's South Pole, investigate the environment and weather there and survey its landform.
Chang'e 8 is tasked with landing near Chang'e 7 on the moon's South Pole, allowing the two missions' components — orbiters, landers, rovers and detectors — to work together to form a prototype of a robotic scientific outpost.
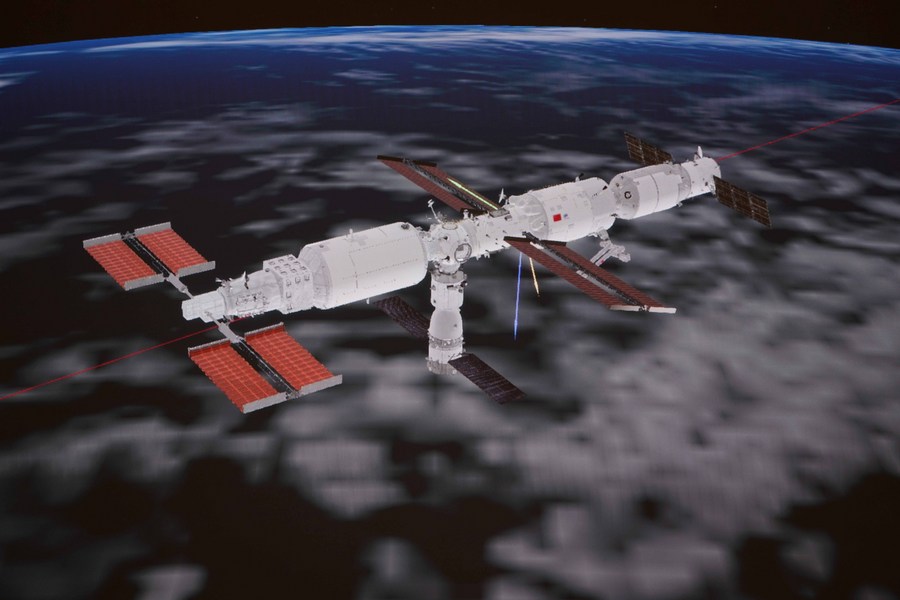

TIANGONG SPACE STATION
A CUTTING-EDGE SPACE-BASED LABORATORY
8
Number of scientific cabinets inside the Wentian science module, mainly used to serve biological and life science studies, and to support research on the growth, aging and genetic traits of plants, animals and microbes in the space environment.
22
Number of extravehicular payload adapters on Wentian's exterior to conduct scientific experiments that require exposure to cosmic rays, vacuums and solar winds.
13
Number of scientific cabinets inside the Mengtian science module — the world's largest single-body spacecraft currently in active service — for microgravity studies and experiments in fluid physics, materials science, combustion science and fundamental physics.
37
Number of extravehicular payload adapters outside Mengtian.
MANNED SPACE MISSIONS
before the in-orbit construction of Tiangong Space Station
Shenzhou V mission Launched on Oct 15, 2003, lasting 21 hours. China's first manned space mission. One crew member.
Shenzhou VI mission
Launched on Oct 12, 2005, lasting nearly five days. China's first multi-staff spaceflight. Two crew members.
Shenzhou VII mission
Launched on Sept 25, 2008, lasting nearly three days. China's first extravehicular activity. Three crew members.
Tiangong I mission
Launched on Sept 29, 2011, lasting about four-and-a-half years. As China's first space laboratory, it received astronauts from the Shenzhou IX and
Shenzhou X missions.
Shenzhou IX mission
Launched on June 16, 2012, lasting nearly 13 days. China's first space docking maneuver (with Tiangong I) and the first time that Chinese astronauts entered a space lab. Three crew members.
Shenzhou X mission
Launched on June 11, 2013, lasting nearly 15 days. During the mission, the first space lecture for Chinese students was made. Three crew members.
Tiangong II mission
Launched on Sept 15, 2016, lasting nearly three years. China's second
space laboratory received astronauts from the Shenzhou XI mission.
Shenzhou XI mission
Launched on Oct 17, 2016, lasting 33 days. The longest stay in space by Chinese astronauts. Two crew members.









